Formatting and Partitioning Flash Drives for FAT32
Modern drives often exceed FAT32's 32GB limit, causing issues in Windows when formatting from exFAT or NTFS. To ensure compatibility with devices requiring FAT32, use DISKPART to create a smaller FAT32 partition and format the remaining space with NTFS or exFAT.

Modern storage drives often exceed the 32GB capacity limit imposed by the FAT32 file system. In Windows, users may encounter difficulties formatting these drives to FAT32 from exFAT or NTFS, as the native formatting tools do not support creating FAT32 partitions larger than 32GB. Additionally, certain devices and BIOS/UEFI firmware may have compatibility issues with exFAT or NTFS, rendering FAT32 a more reliable choice for broader hardware compatibility.
To address this issue, one can utilize the DISKPART utility to create a smaller partition that maintains the FAT32 file system, while allocating the remaining space to a partition formatted with a file system capable of handling larger capacities, such as NTFS or exFAT. This approach ensures compatibility with devices requiring FAT32 while maximizing the usable storage space on the drive.
Here are the detailed steps to achieve this using DISKPART:
Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
Search for "cmd" or "Command Prompt" in the Start menu.
Right-click and select "Run as administrator".
Launch DISKPART:
In the Command Prompt window, type diskpart and press Enter.
List Available Disks:
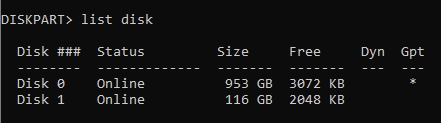
Type list disk and press Enter to display all connected disks.
Select the Target Disk:
Identify the disk you want to partition from the list.
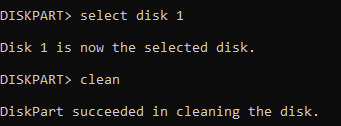
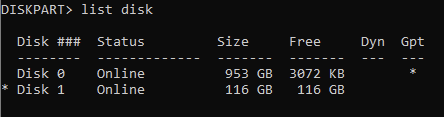
Type select disk X (replace X with the appropriate disk number) and press Enter. You can also clean to remove any previous formatting or partitions. If you aren't sure which disk you have selected you can run list disk again, and notice a * next to the one you are set to modify
FAT32 can only support up to a 32GB partition, and a single file can only support up to 4GB.
Create a Smaller FAT32 Partition:
Enter create partition primary size=32000
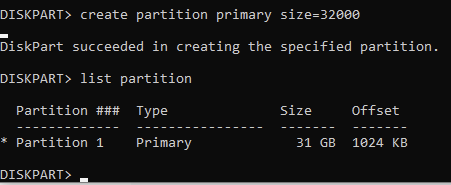
Type format fs=fat32 quick and press Enter to format the newly created partition to FAT32. Optionally, you can also apply a label as well and give it any name you'd like.
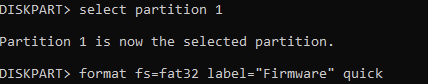
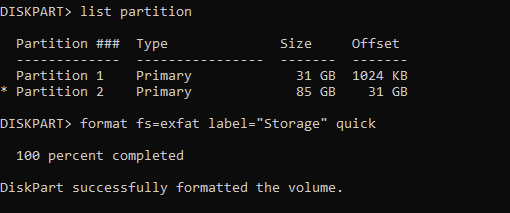
Create a Secondary Partition for Remaining Space:
Type create partition primary to create a second partition using the remaining unallocated space.
Format this partition with a file system capable of handling larger sizes:
- For NTFS: Type
format fs=ntfs quickand press Enter. - For exFAT: Type
format fs=exfat quickand press Enter.
Assign Drive Letters (Optional):
Type assign letter=X (replace X with the desired drive letter) for each partition as needed.
Exit DISKPART:
Type exit and press Enter to close DISKPART.
Type exit again to close the Command Prompt.
This method allows you to leverage the compatibility of FAT32 for specific devices while utilizing the full capacity of modern drives with a more capable file system.



