Editing the Hosts file to connect to local domains

A hosts file is a local file that contains domain names and their matching IPs. It’s found in all common systems. The hosts file itself dates back to around 1982 when it was used in the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), an early version of the Unix operating system. Initially, it was a simple text file named "hosts.txt" that mapped hostnames to IP addresses. This mapping was crucial because, in the early days of networking, computers relied on static tables to resolve hostnames to IP addresses before Domain Name System (DNS) servers became widespread.
The hosts file has its origin in the early days of ARPANET, the precursor to the modern Internet. ARPANET, created by the U.S. Department of Defense in the late 1960s, was the first network to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite.
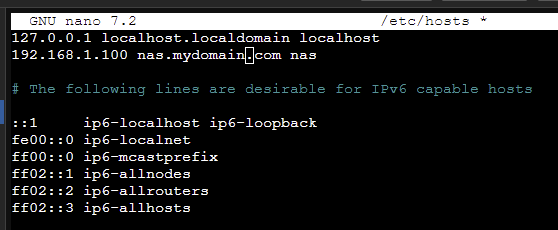
Instead of running and local DNS server or using other routing configurations we can simply edit the hosts file to point to our local network domains.
Windows
Got to your start menu and find Notepad. Right-click to Run as administrator.
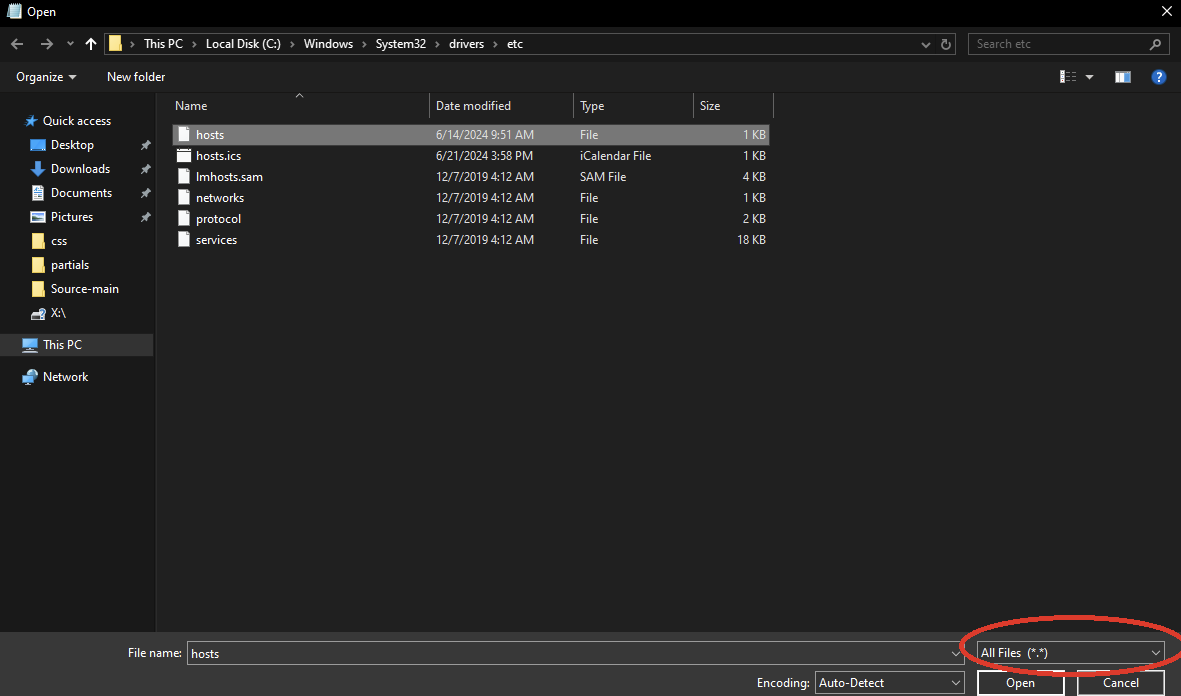
Once in Notepad, go to File -> Open. Get to C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc and make sure to select All Files to find the hosts file.
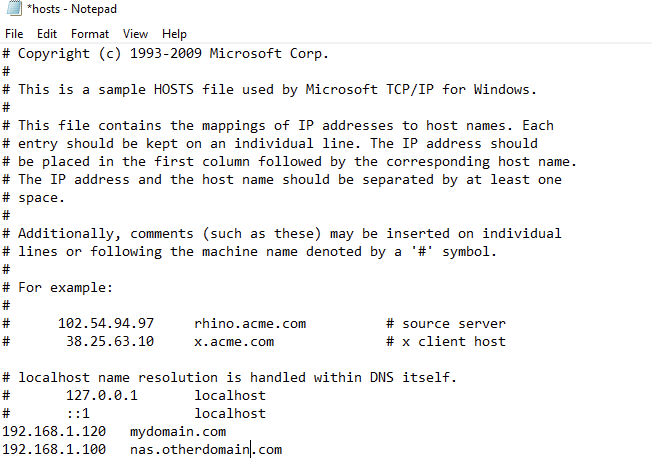
Now you can edit the hosts file and add and IP address and the Domain you want to map it to.
Linux
On most Linux installs you can file the hosts file as /etc/hosts. So you can enter sudo vi /etc/hosts or sudo nano /etc/hosts